zookeeper 的 watcher 机制,可以分为四个过程:
- 客户端注册 watcher。
- 服务端处理 watcher。
- 服务端触发 watcher 事件。
- 客户端回调 watcher。
其中客户端注册 watcher 有三种方式,调用客户端 API 可以分别通过 getData、exists、getChildren 实现,利用前面章节创建的 maven 工程,新建 WatcherDemo 类,以 exists 方法举例说明其原理。
实例
static ZooKeeper zooKeeper;
static {
try {
zooKeeper = new ZooKeeper("192.168.3.39:2181", 4000,new WatcherDemo());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void process(WatchedEvent event) {
System.out.println("eventType:"+event.getType());
if(event.getType()==Event.EventType.NodeDataChanged){
try {
zooKeeper.exists(event.getPath(),true);
} catch (KeeperException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, KeeperException, InterruptedException {
String path="/watcher";
if(zooKeeper.exists(path,false)==null) {
zooKeeper.create("/watcher", "0".getBytes(), ZooDefs.Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE, CreateMode.PERSISTENT);
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("-----------");
//true表示使用zookeeper实例中配置的watcher
Stat stat=zooKeeper.exists(path,true);
System.in.read();
}
}
运行完程序,控制台显示:
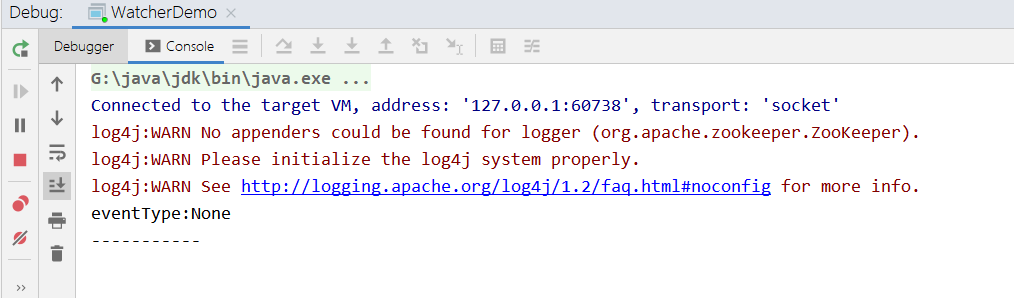
此时启动 zookeeper 命令行终端,查看并且删除 watcher 节点:

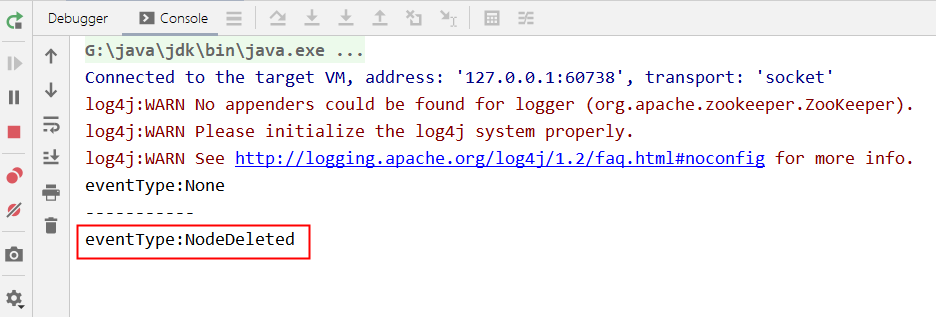
IDE 控制台输出,触发了节点删除事件:
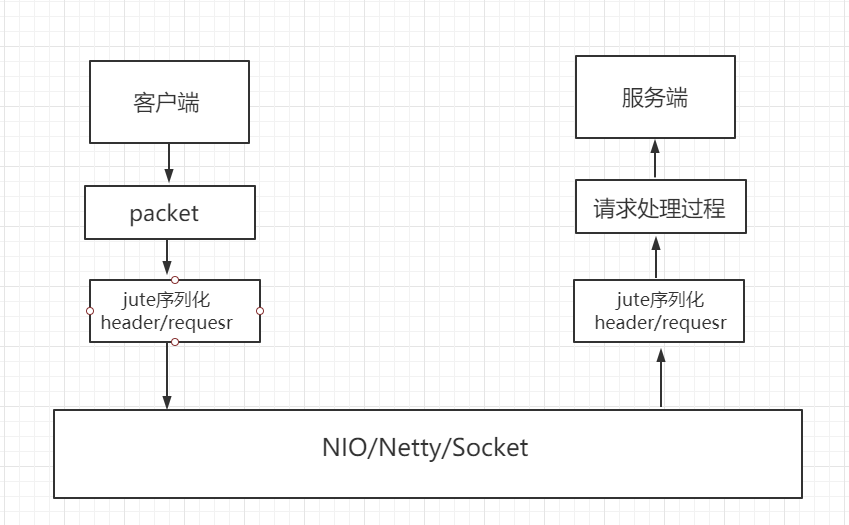
客户端发送请求给服务端是通过 TCP 长连接建立网络通道,底层默认是通过 java 的 NIO 方式,也可以配置 netty 实现方式。
注册 watcher 监听事件流程图:
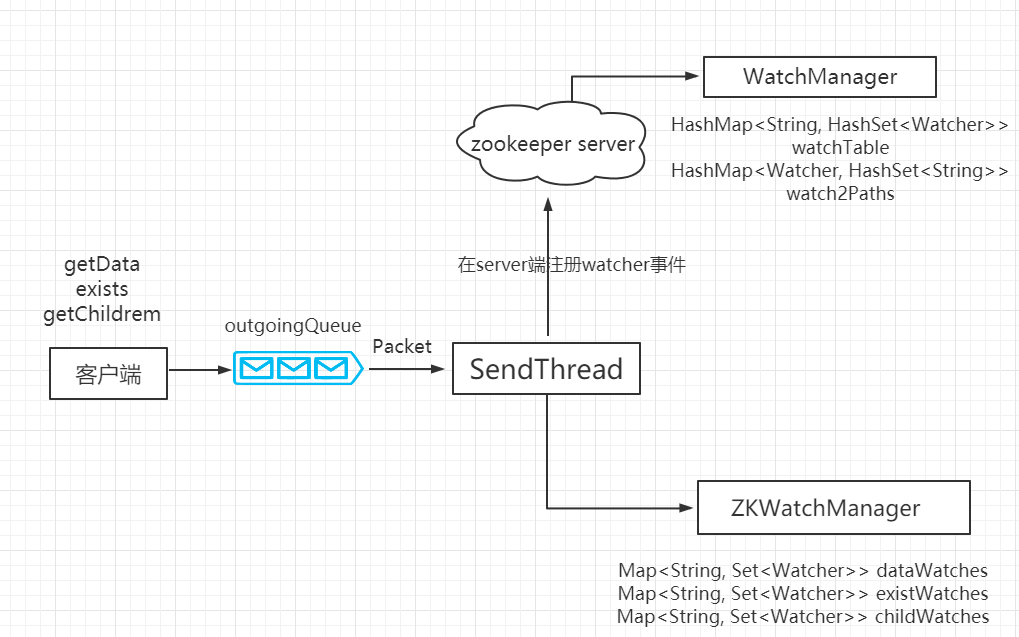
1、客户端发送事件通知请求
在 Zookeeper 类调用 exists 方法时候,把创建事件监听封装到 request 对象中,watch 属性设置为 true,待服务端返回 response 后把监听事件封装到客户端的 ZKWatchManager 类中。
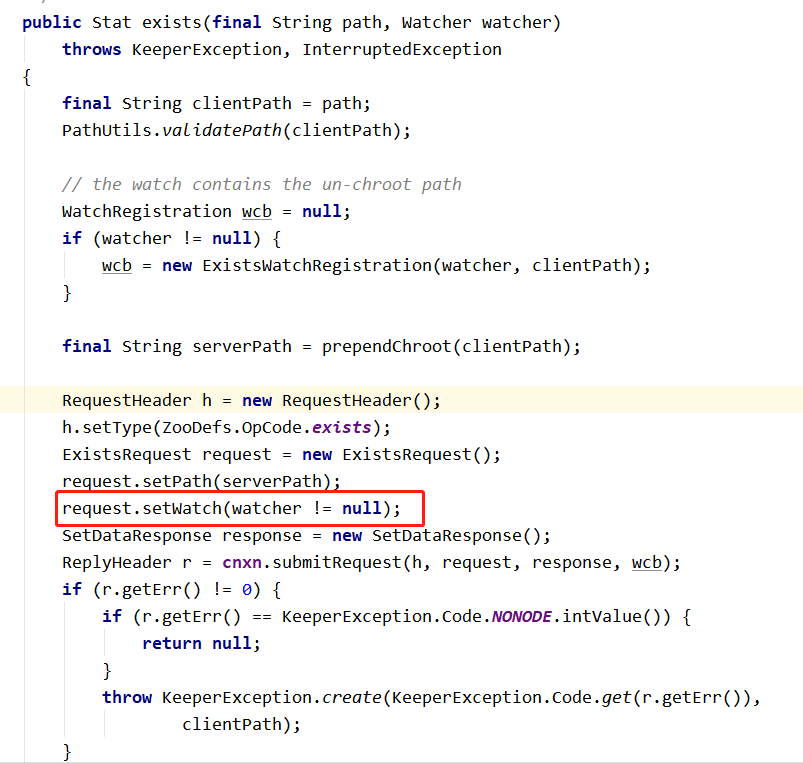
2、服务端处理 watcher 事件的请求
服务端 NIOServerCnxn 类用来处理客户端发送过来的请求,最终调用到 FinalRequestProcessor,其中有一段源码添加客户端发送过来的 watcher 事件:
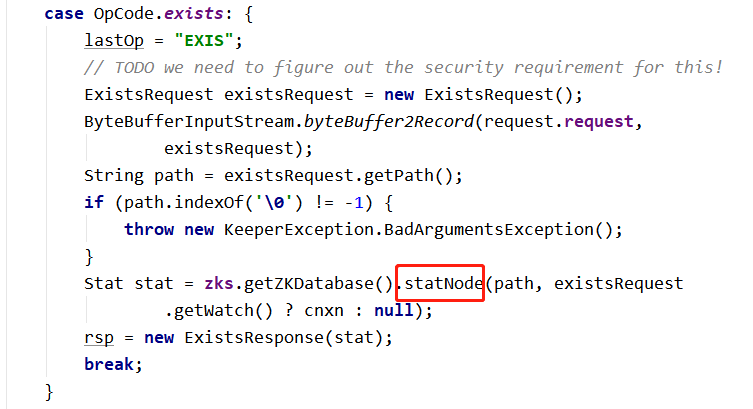
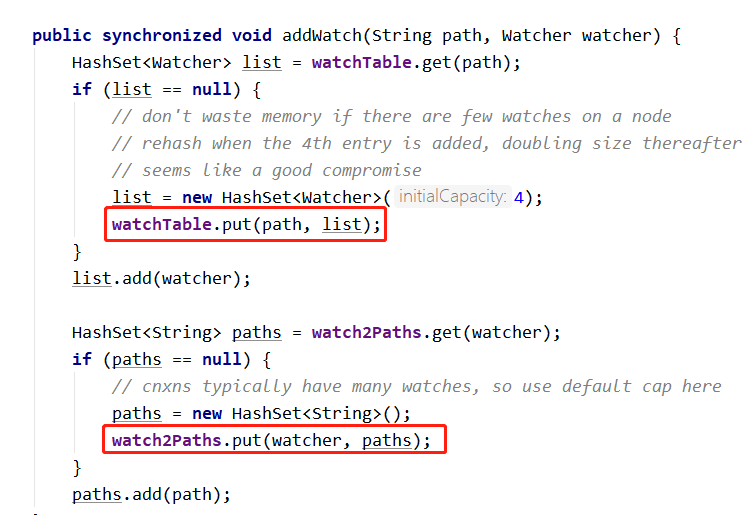
然后进入 statNode 方法,在 DataTree 类方法中添加 watcher 事件,并保存至 WatchManager 的 watchTable 与 watchTable 中。

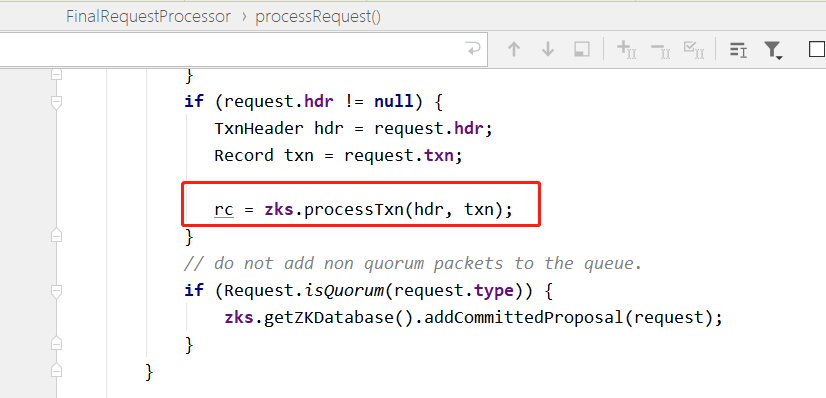
3、服务端触发 watcher 事件流程:
若服务端某个被监听的节点发生事务请求,服务端处理请求过程中调用 FinalRequestProcessor 类 processRequest 方法中的代码如下所示:
删除调用链最终到 DataTree 类中删除节点分支的触发代码段:
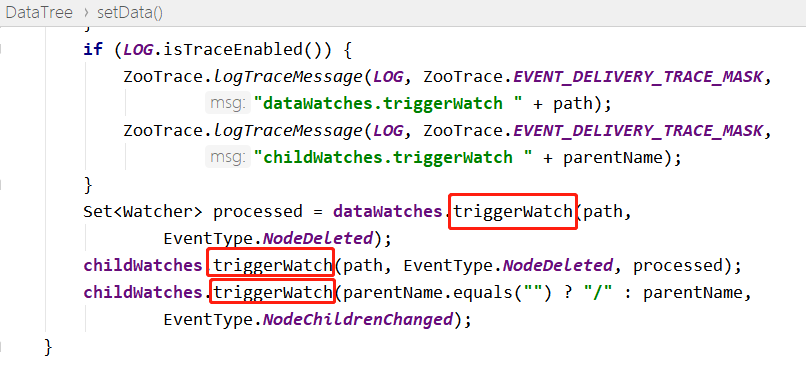
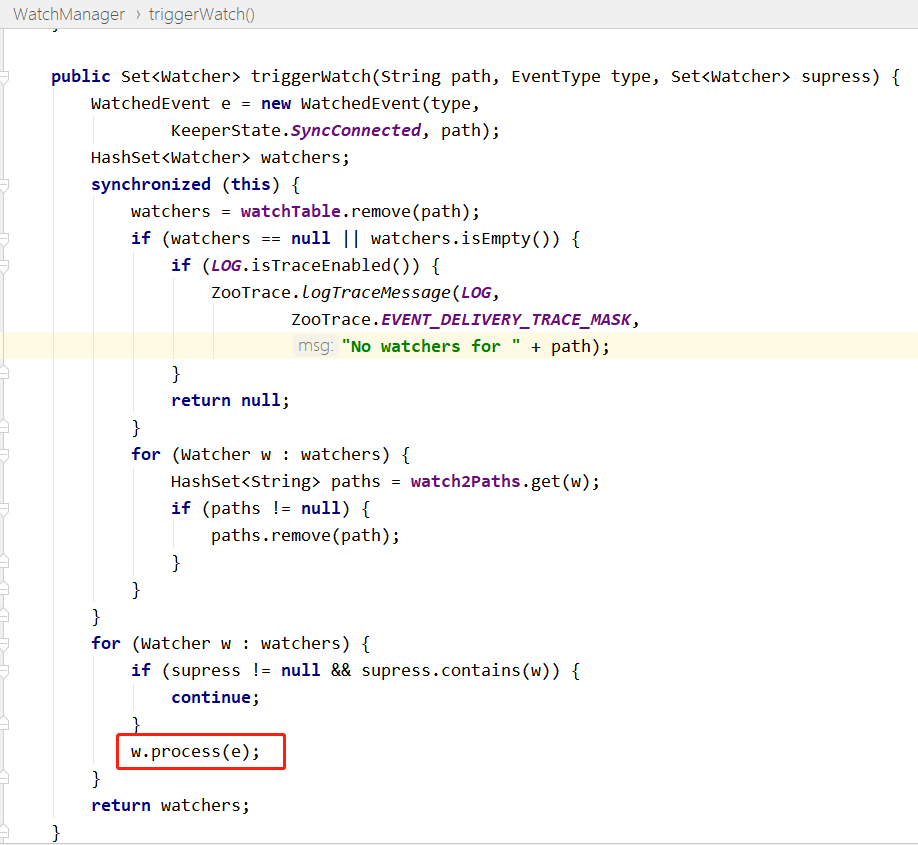
进入 WatchManager 类的 triggerWatch 方法:
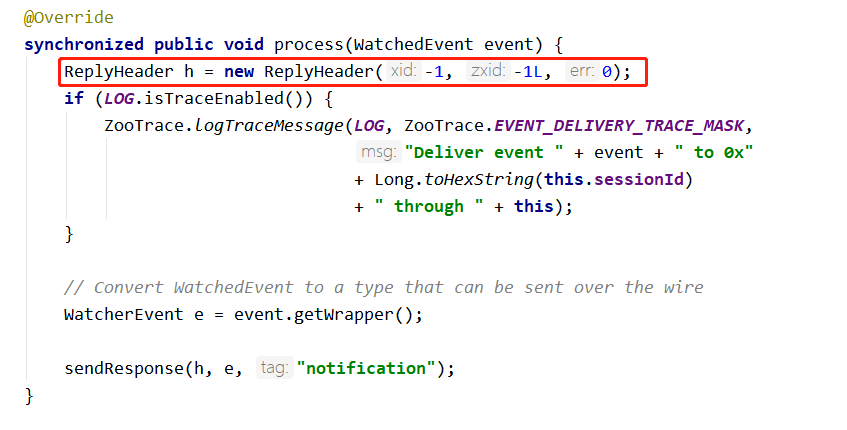
继续跟踪进入 NIOServerCnxn,构建了一个 xid 为 -1,zxid 为 -1 的 ReplyHeader 对象,然后再调用 sendResonpe 方法。
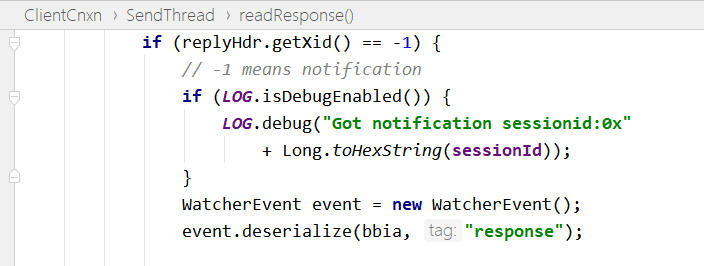
4、客户端回调 watcher 事件
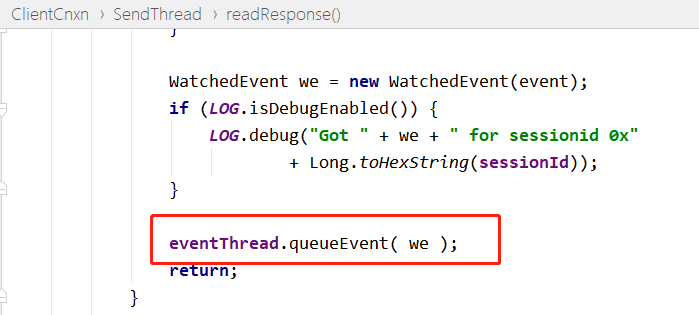
客户端 SendThread 类 readResponse 方法接收服务端触发的事件通知,进入 xid 为 -1 流程,处理 Event 事件。

点我分享笔记